Payal Saxena, MD, from the Department of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, Maryland, USA presents this video case “EUS-Guided Drainage of a Giant Hemorrhagic Pseudocyst by a Through-the-scope Esophageal Metal Stent.”
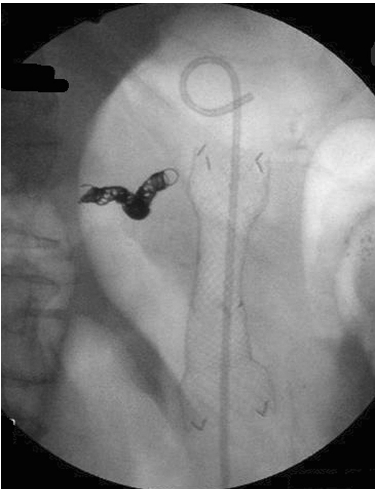
A 78-year-old man with hemorrhagic transformation of a 17cm pseudocyst was hemodynamically unstable requiring splenic artery embolization. He developed gastric outlet obstruction due to the pseudocyst, which was then drained under EUS guidance by creating a cystgastrostomy, flushing the cavity with hydrogen peroxide and placement of a through-the-scope, covered esophageal metal stent (18mm x 60mm) across the cystgastrostomy. A total of 2.4L of blood was drained during the procedure. The patient experienced a rapid resolution of symptoms post-procedure. At 4 week imaging, the pseudocyst had completely resolved after a single procedure. The stent was easily removed with a snare at follow-up endoscopy.
We have demonstrated a novel technique which facilitates safe and rapid resolution of a giant pseudocyst with large volume solid debris (blood clots) without the need for repeated endoscopic procedures, debridement or external drainage. Hydrogen peroxide facilitated dissolution of the blood clots. The wide bore stent allowed passage of debris from the pseudocyst cavity without becoming clogged. The wide caliber covered metal stent also ensured complete seal of the cystgastrostomy tract, preventing complications of leaks and perforation.
A 78-year-old man with hemorrhagic transformation of a 17cm pseudocyst was hemodynamically unstable requiring splenic artery embolization. He developed gastric outlet obstruction due to the pseudocyst, which was then drained under EUS guidance by creating a cystgastrostomy, flushing the cavity with hydrogen peroxide and placement of a through-the-scope, covered esophageal metal stent (18mm x 60mm) across the cystgastrostomy. A total of 2.4L of blood was drained during the procedure. The patient experienced a rapid resolution of symptoms post-procedure. At 4 week imaging, the pseudocyst had completely resolved after a single procedure. The stent was easily removed with a snare at follow-up endoscopy.
We have demonstrated a novel technique which facilitates safe and rapid resolution of a giant pseudocyst with large volume solid debris (blood clots) without the need for repeated endoscopic procedures, debridement or external drainage. Hydrogen peroxide facilitated dissolution of the blood clots. The wide bore stent allowed passage of debris from the pseudocyst cavity without becoming clogged. The wide caliber covered metal stent also ensured complete seal of the cystgastrostomy tract, preventing complications of leaks and perforation.
Fluoroscopic image of the fully covered self expandable metallic stent placed across the cystgastrostomy. A double pigtail stent is seen within the metallic stent. Splenic artery embolization coil is seen to the left of the stent.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
